Five Critical Risks SMEs Face in 2025-2026—And How an AI-Driven Approach Turns Threats into Opportunity
International commerce is surging back to pre-pandemic growth trajectories, yet the very forces that sparked the rebound—digitisation, geopolitical realignment, near-shoring, and volatile monetary policy—have also conspired to create a risk landscape unlike any previous cycle. Small and medium sized enterprises, long celebrated as the lifeblood of global supply chains, confront a paradox: demand for their products is strong, but the financial frictions embedded in cross-border trade threaten to choke liquidity at precisely the moment when these firms must scale, innovate, and seize
new market share.
1 A Shifting Macroeconomic and Regulatory Setting
To appreciate why the five risks described below have intensified, one must start with the macro picture. The International Monetary Fund's April 2025 World Economic Outlook pegs
global trade volume growth at 4.6 percent annually for the next two years— robust, yet materially slower than the double-digit booms of the early 2000s.
Driving that moderation is a patchwork of tariffs, environmental levies, dual-use technology controls, and sanctions programmes that proliferated after 2022. Concurrently, advanced-economy central banks remain divided on inflation strategy: the US Federal Reserve signalled two quarter-point cuts by late 2025, whereas the European Central Bank and Bank of England continue to wrestle with stubborn services inflation, prompting a "higher-for-longer" stance. Such divergence in policy rates has produced violent swings in currency pairs critical to SME exporters—AUD-USD, GBP-EUR, CNY-JPY—forcing treasurers to hedge more frequently and at greater cost. Compounding the challenge, real-time cross-border payment schemes (for example, BIS Project Nexus pilots) are compressing settlement windows, leaving less room to patch errors in trade documentation before funds move
Critical Alert: Cybercrime Evolution
Cybercrime groups have shifted from one-off ransomware attacks to patient infiltration of email threads, logistics portals, and settlement messages—resulting in sophisticated invoice-redirection fraud that masks itself as standard trade workflow. OFAC alone issued over USD 1.6 billion in penalties in 2024 , with several cases implicating SMEs that relied on outdated screening lists.
Against this backdrop, banks must comply with larger capital buffers under Basel III Endgame rules, prioritising low risk, highly transparent trade assets. That means SME deals lacking granular, machine-readable evidence of counterparty health and document integrity endure heavier pricing or outright rejection. Every trend outlined here magnifies one or more of the five headline risks below.
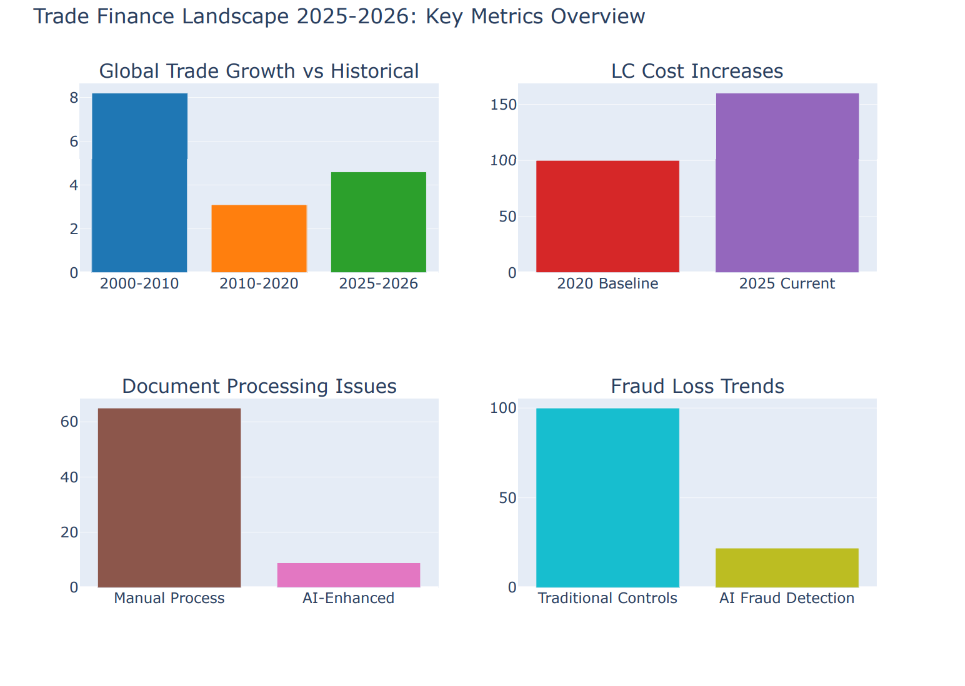
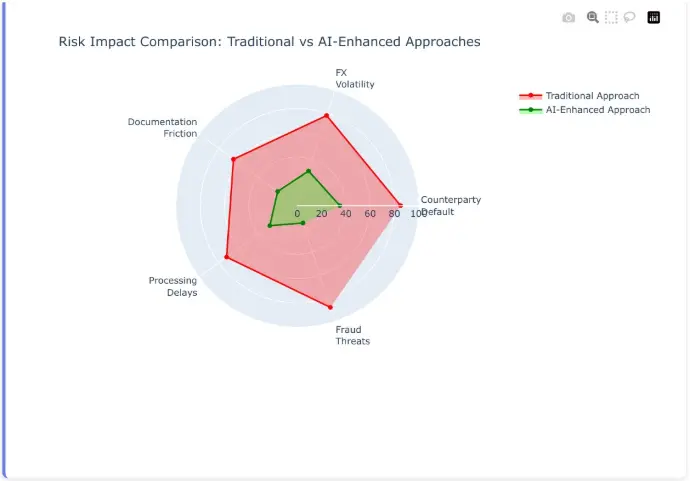
Risk Impact Assessment: The Five Critical Areas
This radar chart reveals the stark difference between traditional risk management approaches and AI-enhanced strategies across the five critical risk dimensions facing SMEs in 2025-2026.
2 Risk One: Counterparty Default and Payment Failure
Why the Threat Is Escalating
Traditional counterparty-credit analysis relies on annual financial statements, sporadic trade-credit bureau updates, and static buyer-seller history. In normal cycles that lag is tolerable, because macro trends are predictable and shock absorption capacity across supply chains is ample. The 2025-2026 window upends those assumptions.
Energy-price spikes can turn a solvent buyer illiquid within a single quarter. Sanctions can halt a distributor's banking access overnight. Monetary tightening in emerging markets can freeze refinancing and trigger a cascade of missed payments across downstream suppliers.
Global insolvency filings have risen by double-digit percentages for two consecutive years
Moreover, global insolvency filings—after pandemic-era moratoria expired—have risen by double-digit percentages for two consecutive years, according to Euler Hermes. SMEs, which typically grant open-account terms to attract overseas customers, bear the brunt. A single unpaid EUR 250,000 shipment can erase annual profit. Worse, because bank capital rules now penalise off-balance-sheet letters of credit issued to thinly capitalised counterparties,
the cost of transferring that risk to an LC has climbed by 50-70 basis points compared to 2020.
The Hidden Cost of Slow Risk Recognition
When a buyer's payment capacity deteriorates, the first red flags appear in operational datasets—partial purchase order cancellations, unusual credit-term negotiations, or frequent shipping delivery deferrals. Yet many SMEs lack the analytics to synthesise those signals. By the time a formal credit insurer downgrades the buyer, goods may already be in transit, obligating the seller to fulfil contractual delivery at the worst possible time.
Financial Impact Analysis
Researchers at the Asian Development Bank estimate that
late payment alone adds 13 days to the cash-conversion cycle for APAC exporters. Add formal default
and the median cash-loss recoupment timeline stretches past 12 months, as claims wend through under resourced courts.
For SMEs operating on margins of 5-8 percent, each percentage point of unpaid revenue eliminates nearly 20 percent of free cash flow, constricting R&D, hiring, and marketing budgets that power long-run competitiveness.
AI-Enabled Mitigation Strategies
A new generation of machine-learning credit-insight engines, trained on granular trade data, offers a materially different approach. These platforms ingest invoices, shipping milestones, customs filings, third-party financial records, and macro signals such as commodity prices or policy-rate changes. They then produce dynamic risk scores updated daily, not quarterly.
Importantly, leading systems incorporate explainability modules. Rather than outputting a black-box score, they surface the key drivers—inventory turnover slowdown, FX mismatch, regulatory action—allowing finance teams to override or adjust exposure thresholds with auditable justification. That matters under evolving AI-governance rules in the EU and Australia, which emphasise traceable decision flows.
Early adopters report a 35% reduction in payment-default incidence and 4.1-day improvement in DSO
In practice, SMEs that embed such AI tools into their ERP trigger bespoke actions when risk crosses preset thresholds: shifting from open-account to LC terms; splitting orders into smaller tranches; or purchasing short-tenor trade-credit insurance programmatically through digital brokers. Early adopters report a 35 percent reduction in payment-default incidence relative to peers, translating into an average 4.1-day improvement in DSO and a two-notch uplift in bank credit ratings, which in turn lowers borrowing costs across the board.
3 Risk Two: Foreign-Exchange Volatility and Settlement Timing
Structural Drivers of FX Turbulence
The 2025-2026 period coincides with a rare synchrony of structural FX drivers: divergent central-bank cycles, climate policy-linked commodity price swings, and geopolitical realignment that redirects capital flows from North-South to South-South corridors. Currency pairs once considered stable—such as SGD-USD or CAD-USD—
exhibit intraday swings exceeding 1 percent , a threshold that can wipe out product margin on low-value-add
manufactured goods.
Meanwhile, real-time payment rails (for example, FedNow linkage with the MAS FAST network) settle cross-border exposures in seconds, collapsing the historical buffer window during which SMEs could execute manual FX conversions. The mismatch between invoice issuance, shipping, customs clearance, and final payment creates open exposures that treasury teams often track in spreadsheets—tools ill-suited to millisecond market moves.
Cost Implications of Unhedged Exposures
SMEs surrender on average 2.3% of revenue annually to currency slippage and ad-hoc hedging fees
Accenture's 2024 Global Treasury Benchmark shows that SMEs without active FX-risk programmes surrender on average 2.3 percent of revenue annually to currency slippage and ad-hoc hedging fees. That erosion exceeds the typical net profit of many light-manufacturing exporters. Furthermore, rating agencies consider unhedged FX policy a governance weakness, elevating credit-risk premiums.
Cash-flow uncertainty also hampers operational decision-making. Procurement cannot commit to bulk raw-material orders if the expected currency in-flows might fall short by month-end. Sales teams struggle to quote firm prices beyond 30 days. The cumulative effect is a competitive disadvantage relative to multinationals that deploy advanced treasury management systems.
AI-Centric Hedging and Exposure-Management Solutions
State-of-the-art AI treasuries track exposures at the invoice and purchase-order line level, pulling data from ERP, shipping, and banking feeds. Natural-language processing tags currency amounts buried within unstructured PDF contracts, while deep-learning models forecast currency trajectories conditioned on central-bank speech sentiment, satellite-derived trade-flow data, and even social-media chatter around political instability.
Such predictions feed rules-based hedging engines. When threshold deviation probability surpasses a preset confidence level, the system auto-executes forward contracts or dynamic collar strategies through an integrated FX liquidity aggregator, spreading transactions across multiple banks for best execution.
SMEs slash manual hedge-execution time from 3 hours per day to mere minutes with 60-basis-point average exchange-gain improvement
SMEs deploying these tools slash manual hedge-execution time from three hours per day to mere minutes, while internal back-testing indicates a 60-basis-point average exchange-gain improvement versus passive hedging. Over a two-year horizon, that can equate to six figures of preserved EBITDA for a mid-size exporter invoicing USD 20 million annually.
4 Risk Three: Documentation and Compliance Friction
Regulatory Tightening Across Jurisdictions
Since 2023, regulators have broadened the scope of dual-use goods controls, tightened beneficial-ownership reporting, and ramped fines for sanctions breaches to eye-watering levels. The US OFAC alone issued over USD 1.6 billion in penalties in 2024, with several cases implicating SMEs that relied on outdated screening lists. In parallel, European Union's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) introduces complex emissions-intensity declarations at customs. Each new rule adds pages of data fields, certificates, and declarations required for cross-border clearance.
The Operations Tax of Manual Document Handling
A typical APAC SME exporter juggles a bill of lading, commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, inspection certificates, CBAM declarations, and multiple bank forms. Each document must reconcile dozens of data points—HS codes, shipping weights, consignee addresses—without error. Traditional workflow involves scanning, emailing, re keying into bank portals, and couriering hard copies.
Manual document discrepancies affect nearly 65% of LC presentations, extending payment release by up to 7 days
Studies by the International Chamber of Commerce suggest that manual document discrepancies affect nearly 65 percent of LC presentations, forcing rework that extends payment release by up to seven days. Multiply that delay by interest on revolving credit lines and the intangible cost of staff overtime, and documentation drag can add 1-2 percent to cost of goods sold.
AI Document Intelligence and Automated Compliance
Recent breakthroughs in computer vision and transformer-based language models enable near-human-level extraction of data from semi-structured trade documents. Where legacy optical-character-recognition tools struggled with non standard templates or overlapping stamps, modern AI systems learn field placement contextually, then cross-validate against a digital rulebook that encapsulates ICC Uniform Customs and Practice (UCP 600) clauses, local customs regulations, and sanctions lists.
When the engine detects a discrepancy—say, a weight mismatch between the bill of lading and packing list—it flags the anomaly, references the precise rule breached, and suggests corrective wording. Integration with e-signature platforms lets counterparties approve amendments instantly, reducing iteration cycles.
Early adopter SMEs report a 70% reduction in presentation errors and 40% cut in time-to-payment
Early adopter SMEs report a 70 percent reduction in presentation errors and a 40-percent cut in time-to-payment. Notably, such improvement satisfies banking partners that must evidence robust Know-Your-Customer (KYC) and Know-Your-Transaction (KYT) controls to regulators, leading to preferential LC pricing.
5 Risk Four: Instrument Processing Delays—Letters of Credit, Guarantees, and Beyond
Legacy Workflow Bottlenecks
Despite digitisation, many banks rely on siloed systems: LC issuance handled in one platform, amendments in another, compliance checks in a third, with little real-time synchronisation. Every discrepancy query reenters a queue that may already exceed service-level commitments. The consequence is a multi-week lag between pro-forma invoice and LC opening, compressing shipment planning windows and forcing SMEs to hold buffer inventory or chase expensive last mile logistics options.
Guarantees fare no better. Construction-project SMEs often wait ten working days for a performance guarantee because banks require manual collateral assessment and board approval, even for repeat customers. In volatile markets, such delays can invalidate bid deadlines.
Capital-Based Incentives for Banks to Prioritise Digital Trade
Basel III Endgame differentiates trade instruments by granularity of transaction data and traceability. Banks that capture machine-readable shipment and compliance proof can assign lower credit-conversion factors. Consequently, financial institutions are keen to migrate customers to digital-first instruments—provided the customer can supply clean, standardised data.
AI-Assisted LC Assembly, Validation, and Lifecycle Management
Forward-thinking SMEs are partnering with fintech platforms embedding AI rules engines directly into LC assembly screens. The seller uploads commercial terms; the software autocompletes ICC-compliant clauses, dynamic expiry buffers, and port codes, referencing a template library curated in collaboration with major correspondent banks.
Machine-learning models analyse historical discrepancy patterns across millions of LCs, recommending wording adjustments that cut rejection probability. Once issued, the LC lives as a smart object: each shipping milestone— container gate-in, customs release, proof of delivery—updates the LC status. Bank and seller dashboards align, letting either party request and process amendments in near-real time.
Pilot programmes report average LC cycle-time reduction from 10.2 to 5.8 days
Quantitatively, pilot programmes in Singapore report average LC cycle-time reduction from 10.2 to 5.8 days—a saving that frees working capital and compresses lead-time variability, critical for just-in-time manufacturing. As a bonus, banks reward the improved risk profile with lower confirmation fees, cascading benefits through the supply chain.
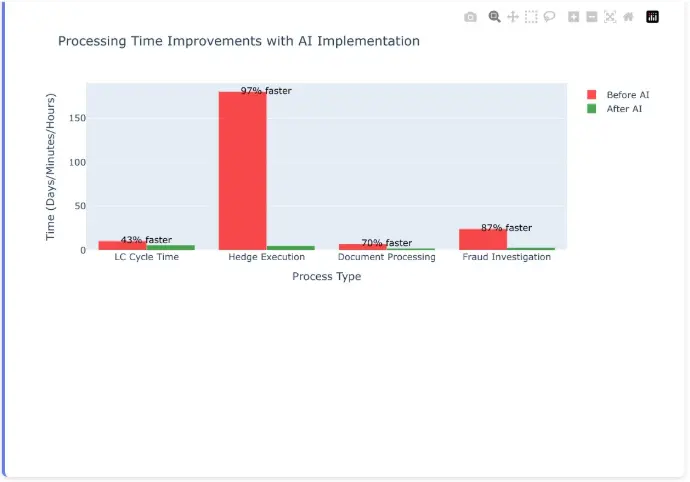
Processing Time Improvements with AI Implementation
Dramatic reductions in processing times across key trade finance operations when AI-enhanced systems replace traditional manual processes.
6 Risk Five: Fraud and Identity Threats in Digital Trade Channels
Evolution of Attack Vectors
Cybercriminals have pivoted from brute-force ransomware toward business-email-compromise schemes, supply-chain infiltration, and deep-fake identity manipulation. In one 2024 case involving a UK auto-parts SME, attackers spoofed the CEO's voice during a conference call, instructing treasury to redirect LC proceeds to a Hong Kong account. Losses exceeded GBP 320,000 before insurers capped recovery.
Simultaneously, the shift to paperless trade and remote work expands the attack surface: shared drives, electronic bill of-lading portals, and freight apps provide multiple entry points. Traditional fraud controls—manual callback verification, PDF stamp authenticity checks—are inadequate against AI-generated documents and voices.
Quantifying the Financial Drag
Median direct fraud loss: USD 140,000 per incident for SMEs in trade channels
The Association of Certified Fraud Examiners estimates that median direct fraud loss for SMEs in trade channels stands at USD 140,000 per incident. Yet collateral damage is greater: banks may de-risk a client if repeated fraud suggests weak controls, raising lending spreads by 150-200 basis points or terminating facilities entirely. Reputational damage can scupper new distribution contracts, especially in regulated industries such as pharmaceuticals or chemicals.
Multi-Signal AI Fraud Detection and Transaction Anomaly Scoring
Best-practice defences combine AI models that fuse document forensics (pixel inconsistency, compression artefacts), behavioural analytics (login time, device fingerprinting), and graph-based network analysis that maps counterparties across previous shipments, bank accounts, and IP addresses. A sudden appearance of a new bank beneficiary linked indirectly to a sanctioned entity triggers real-time payment holds, pending human review.
Moreover, deep-fake detection algorithms trained on facial-movement inconsistencies analyse video-KYC calls, while voice-synthesis classifiers score phone instructions for authenticity. These tools feed a central risk-orchestration engine that enforces step-up authentication—video callback, notarised document upload—when composite risk crosses a threshold.
AI-driven fraud orchestration achieves 78% cut in successful invoice-redirect fraud
Implemented properly, AI-driven fraud orchestration reduces false-positive rates versus rule-based systems, sparing legitimate customers friction. Data from an Australian fintech consortium shows a 78-percent cut in successful invoice redirect fraud across 2,200 SME users, alongside a 22-percent reduction in manual compliance workload, because analysts triage fewer alerts.
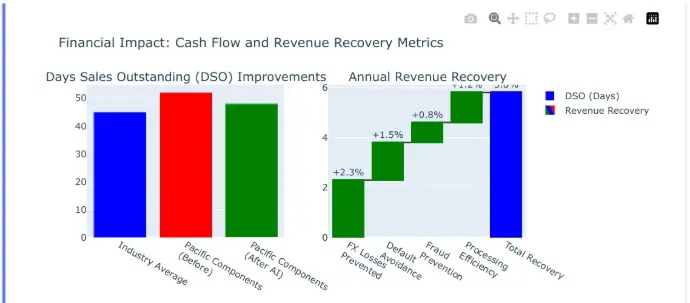
Financial Impact: Cash Flow and Revenue Recovery Metrics
Quantified improvements in key financial metrics showing how AI implementation transforms cash flow management and revenue protection for SMEs.
7 Beyond Point Solutions: Building an Integrated AI-First Trade-Finance Operating Model
Addressing each risk in isolation yields incremental gains; true competitive advantage arises when SMEs weave AI, data, and human expertise into a unified trade-finance fabric. Such an operating model features the following pillars.
First, a single source of truth for transaction data. Whether orders originate in an e-commerce storefront, an EDI feed, or a manual purchase-order PDF, all relevant attributes flow into a central ledger. API connectors push updates to logistics platforms, treasury tools, and bank portals, ensuring that every stakeholder works from real-time, reconciled data.
Second, policy automation grounded in domain-specific ontologies. Instead of generic machine-learning models, leading platforms encode ICC rules, Incoterms nuances, and jurisdiction-specific customs regulations into knowledge graphs that guide decisions. The result is human-interpretable AI that compliance officers can audit.
Third, human-in-the-loop oversight. AI proposes risk scores and hedging actions, yet final authority remains with finance or compliance managers who validate high-impact steps. Crucially, the system logs every override with rationale, satisfying both internal audit and external regulators.
Fourth, continuous learning via feedback loops. Each discrepancy corrected, fraud attempt blocked, or hedge executed feeds new data into model retraining pipelines, gradually enhancing precision and recall. SMEs thereby accumulate proprietary risk-intelligence moats that are difficult for laggard competitors to replicate.
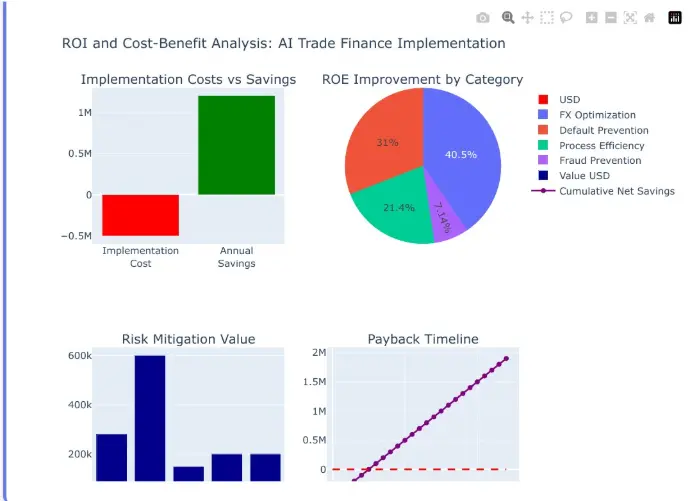
ROI and Cost-Benefit Analysis: AI Trade Finance Implementation
Comprehensive analysis of implementation costs versus savings, showing the strong business case for AI-driven trade finance transformation and typical payback timelines.
8 Real-World Impact: A Composite SME Case Study
Consider "Pacific Components," a fictional but data-grounded mid-size Australian electronics exporter supplying OEMs in Vietnam, Germany, and the United States. Pre-digital transformation, the firm grappled with
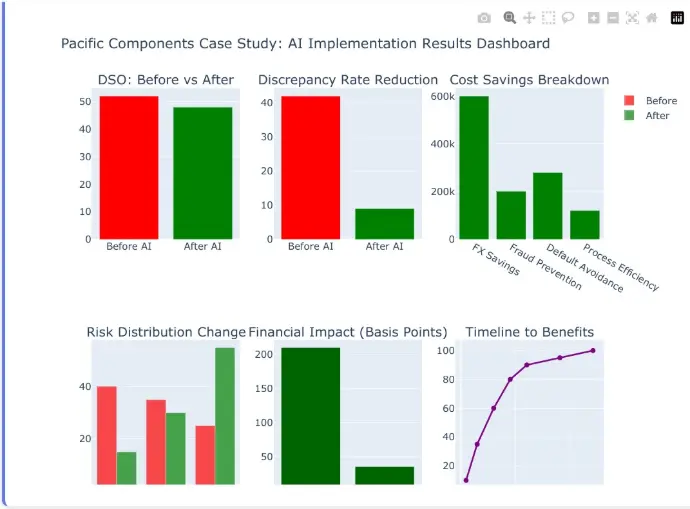
52-day DSO, 8-percent annual revenue loss to FX slippage and unpaid invoices, and a USD 1.2 million LC- confirmation fee bill.
After implementing an AI-first trade-finance stack:
- Dynamic counterparty scoring flagged an early solvency warning on a German buyer; Pacific shifted that order to secured terms, avoiding a EUR 280,000 loss when the buyer later filed for protection.
- Real-time FX-exposure capture and automated hedging clipped annual slippage to under 1 percent, saving AUD 600,000.
- AI document intelligence dropped LC discrepancy rate from 42 percent to 9 percent, shrinking payment release lag by four days.
- Fraud orchestration caught a convincingly spoofed invoice reroute, preventing AUD 200,000 from vanishing.
Overall: Pacific Components improved ROE by 210 basis points and negotiated a 35-basis-point lower revolving credit spread
Overall, Pacific Components improved ROE by 210 basis points and negotiated a 35-basis-point lower revolving credit spread, attributing both gains directly to quantifiable risk reduction.
Pacific Components Case Study: AI Implementation Results Dashboard
Detailed performance metrics from Pacific Components' AI transformation journey, showcasing tangible improvements
across all key risk and performance indicators.
9 Conclusion: Turning 2025-2026 Uncertainty into Strategic Advantage
The next two years will doubtless test the resilience of SMEs active in cross-border trade. Yet the same dynamics that create peril also hand forward-thinking management teams an historic opportunity. Counterparty volatility rewards those who ingest real-time data and adjust credit terms dynamically. FX turbulence favours treasuries that automate hedging. Regulatory complexity penalises paper-centric documentation yet advantages AI forms that prove compliance instantly. Instrument delays bedevil firms stuck in legacy bank queues but melt away for those who co create digital LC pathways. Fraud becomes a threat only to enterprises whose controls begin and end with human intuition; it becomes a nuisance to those layering multi-signal AI detection.
Collectively, the five risks outlined—counterparty default, currency volatility, documentation drag, instrument delay, and digital fraud—need not decimate margin or growth plans. They can, when managed through an integrated AI-first operating model, become levers for superior cash-flow velocity, stronger banking relationships, and brand differentiation grounded in reliability. Investors increasingly reward such operational sophistication, rating agencies view it as governance strength, and customers prefer suppliers who can promise—and deliver—on-time product with minimal administrative overhead.
Call to Action
The call to action is clear: audit your current trade-finance workflow end-to-end, map each step to the corresponding risk dimension, and pilot AI-enabled controls that close the highest-impact gaps first. In the process, you will join a vanguard of SMEs redefining what "small" and "medium" mean in global trade—firms whose agility is matched by risk intelligence, and whose size is no barrier to operating at the frontier of finance technology.
The window to act is now; the next shipment you dispatch should already be protected by the future of trade-finance risk management.
This enhanced article features interactive data visualizations and comprehensive analysis of trade finance risks facing SMEs in 2025-2026.
The integrated charts provide actionable insights into AI-driven risk mitigation strategies and quantified performance improvements.
Navigating the New Era of Trade Finance